Introduction
The Project Start-Up phase is a crucial part of the project management, setting the foundation for a successful project. Often misunderstood or conflated with the initiation phase, Project Start-Up involves distinct activities aimed at ensuring that a project is feasible, valuable, and aligned with organizational goals before significant resources are committed. There is a need to also have understood the fundamentals of project management in order to understand and use right domain glossary of terms.
During Project Start-Up, key roles are assigned, initial project definitions are established, and essential documents like the Project Brief and Outline Business Case are created. This phase is all about getting things right from the outset, providing a clear direction and framework for the project to follow.
Understanding the importance of Project Start-Up can significantly enhance the likelihood of project success. It allows organizations to avoid unnecessary expenditures on projects that are not well-conceived and ensures that all stakeholders are on the same page from the very beginning.
You can also download a Free Project Startup Document Checklist here, for additional information.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the various components of the Project Start-Up phase, exploring key activities, documents, and best practices to ensure a smooth and effective start to your projects.
Table of Contents
Understanding Project Start-Up

The Project Start-Up phase is designed to lay a solid foundation for a project’s success. This phase occurs before the project initiation and involves preliminary planning to ensure that the project is feasible, aligned with organizational goals, and has clearly defined objectives.
What is Project Start-Up?
Project Start-Up is the initial phase where key groundwork is established before fully committing to a project. It is a pre-project process, designed to ensure that the prerequisites for initiating the project are in place. The process expects the existence of a Project Mandate that defines in high-level terms the reason for the project and what product is required.
It is important to know the essential project documents for each phase. You can also Download a Free project documentation checklist here.
The aim is to ensure that there is a clear understanding of the project’s purpose, scope, and feasibility. During this phase, critical decisions are made about whether or not to proceed with the project.
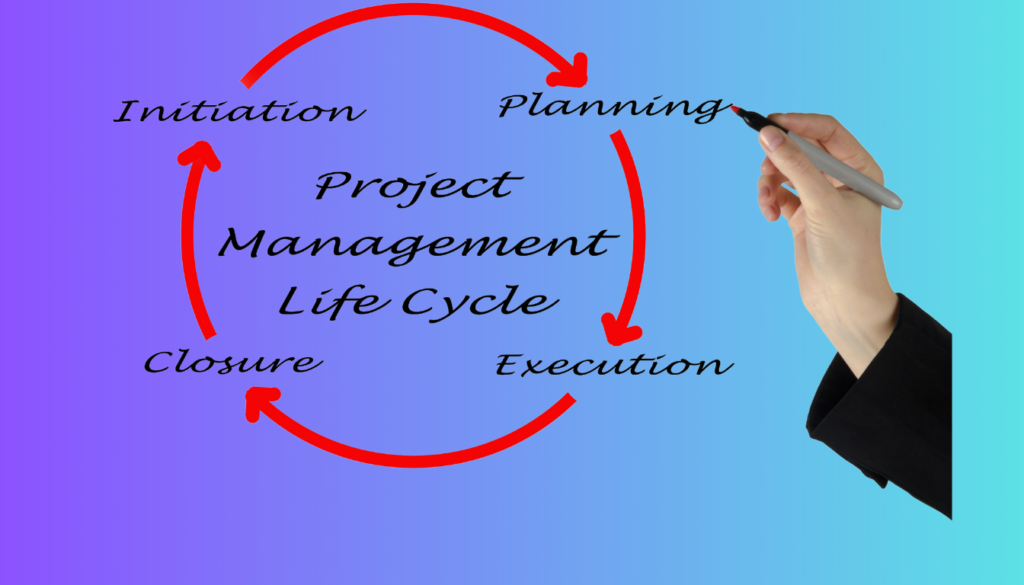
Importance of Project Start-Up
The phase is crucial for several reasons:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Clarity | Ensures that everyone involved understands the project’s purpose and objectives. |
| Alignment | Aligns the project with the organization’s strategic goals. |
| Risk Mitigation | Identifies potential risks early and allows for the development of mitigation strategies. |
| Resource Allocation | Ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and effectively from the start. |
Objectives of Project Start-Up
Define Project Objectives
Clearly outline what the project aims to achieve.
Establish Key Roles
Assign roles such as the Executive and Project Manager to ensure leadership and accountability.
Develop Initial Plans
Create initial project documents like the Project Brief and Outline Business Case.
Assess Feasibility
Evaluate whether the project is viable and aligns with organizational strategy.
Secure Commitment
Ensure that there is commitment from key stakeholders before moving forward.
Key Activities in Project Start-Up
| Key Activities in Project Start-Up | Description | Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Appointing Key Roles | Identify and assign key roles such as the Executive and Project Manager. | – Assign the Executive for strategic direction and oversight. – Appoint the Project Manager for day-to-day project management. |
| Designing the Project Management Team | Form a project management team with clearly defined roles and responsibilities. | – Identify team members with necessary skills. – Define roles and responsibilities. – Establish a clear reporting structure. |
| Preparing the Project Brief | Develop a document that outlines the project’s objectives, scope, and deliverables. | – Include objectives, scope, deliverables, constraints, assumptions, and initial risks. |
| Creating the Outline Business Case | Provide a preliminary justification for the project, outlining the expected benefits, costs, and risks. | – Include project rationale, benefits, costs, risks, and initial feasibility analysis. |
| Selecting the Project Approach | Determine the overall approach and methodology that will be used for the project. | – Evaluate different methodologies (e.g., Agile, Waterfall). – Select the most suitable approach. – Outline project management processes. |
Preparing the Project Brief
In this phase, one of the most crucial tasks is preparing the Project Brief. The Project Brief serves as the foundational document that outlines the project’s purpose, scope, objectives, and deliverables. It provides a clear direction for the project and ensures that all stakeholders are aligned from the outset.
What is a Project Brief?

A Project Brief is a high-level document that summarizes the essential aspects of a project. It includes key information about the project’s objectives, scope, deliverables, assumptions, constraints, and initial risks. The Project Brief serves as a reference point throughout the project lifecycle and helps in securing approval to proceed to the initiation phase.
Key Components of a Project Brief
| Key Components of a Project Brief | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Project Objectives | Clearly define what the project aims to achieve. Objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). | Ensures all stakeholders have a common understanding of the project’s goals. |
| Project Scope | Outline the boundaries of the project, including what is included and excluded. | Helps prevent scope creep by clearly defining the project’s limits. |
| Project Deliverables | List the specific outputs or products that the project will produce. | Provides a clear understanding of what will be delivered to the stakeholders upon project completion. |
| Assumptions and Constraints | Identify any assumptions that have been made and any constraints that may impact the project. | Ensures that potential limitations and dependencies are considered from the start. |
| Initial Risks | Highlight any potential risks that could affect the project’s success. | Allows for early risk identification and the development of mitigation strategies. |
| Project Approach | Describe the overall approach and methodology that will be used to manage the project. | Ensures that there is a clear strategy for how the project will be executed and managed. |
Steps to Prepare a Project Brief
| Steps to Prepare a Project Brief | Description |
|---|---|
| Gather Information | Collect all relevant information about the project, including stakeholder requirements, organizational goals, and any existing documentation. |
| Define Objectives and Scope | Clearly outline the project’s objectives and scope, ensuring they align with the organization’s strategic goals. |
| Identify Deliverables | List all the deliverables that the project will produce, ensuring they are specific and measurable. |
| Assess Assumptions and Constraints | Identify any assumptions and constraints that may impact the project and document them. |
| Evaluate Risks | Conduct an initial risk assessment to identify potential risks and develop preliminary mitigation strategies. |
| Draft the Project Brief | Compile all the gathered information into a cohesive document, ensuring clarity and conciseness. |
| Review and Validate | Share the draft Project Brief with key stakeholders for review and validation. Make necessary revisions based on their feedback. |
Developing the Outline Business Case
During the Project Start-Up phase, one of the essential tasks is developing the Outline Business Case. This document serves as a preliminary justification for the project, outlining the expected benefits, costs, and risks. It helps decision-makers understand the value and feasibility of the project before committing significant resources.
What is an Outline Business Case?
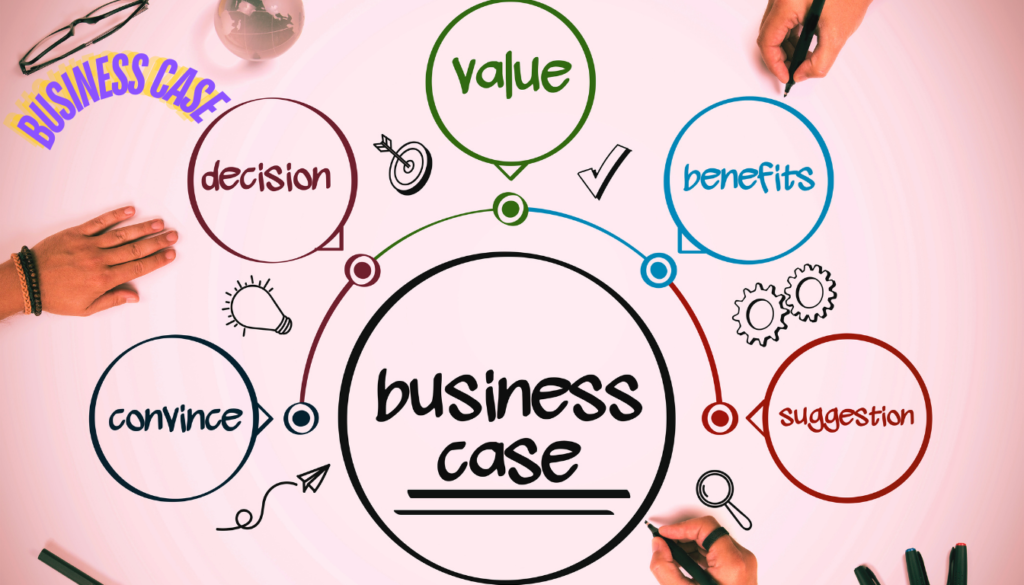
An Outline Business Case is a high-level document that provides an initial assessment of the project’s viability. It includes key information about the project’s objectives, expected benefits, costs, risks, and alignment with organizational goals. The Outline Business Case is crucial for obtaining approval to move forward with the project.
Key Components of an Outline Business Case
| Component | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Project Rationale | Explain why the project is being proposed, including the problems it aims to solve or the opportunities it seeks to capitalize on. | Provides a clear understanding of the project’s purpose and necessity. |
| Expected Benefits | Outline the tangible and intangible benefits the project is expected to deliver, such as increased revenue, cost savings, or improved customer satisfaction. | Helps stakeholders understand the value the project will bring to the organization. |
| Cost Estimates | Provide an initial estimate of the project’s costs, including capital expenditures, operational costs, and any other associated expenses. | Ensures that decision-makers are aware of the financial investment required for the project. |
| Risk Assessment | Identify potential risks that could impact the project’s success and outline preliminary mitigation strategies. | Helps in understanding the risks involved and planning for their management. |
| Alignment with Organizational Goals | Demonstrate how the project aligns with the strategic objectives and goals of the organization. | Ensures that the project supports the broader mission and vision of the organization. |
| Feasibility Analysis | Assess the project’s feasibility in terms of technical, financial, and operational aspects. | Provides an initial check on whether the project is practical and achievable. |
Steps to Develop an Outline Business Case
- Identify Project Needs: Understand the underlying needs or opportunities that the project aims to address.
- Gather Data: Collect relevant data on potential benefits, costs, and risks associated with the project.
- Draft the Document: Compile the gathered information into a structured document, covering all key components.
- Review and Refine: Share the draft with key stakeholders for feedback and make necessary revisions.
- Seek Approval: Present the finalized Outline Business Case to decision-makers to obtain approval to proceed.
Project Product Description
Creating a detailed Project Product Description is essential for defining what the project will deliver. This document provides a clear and comprehensive description of the project’s end product, ensuring that all stakeholders have a shared understanding of the project’s goals and deliverables.
What is a Project Product Description?

A Project Product Description is a detailed document that outlines the characteristics, purpose, and criteria for the project’s final deliverable. It serves as a reference throughout the project lifecycle, ensuring that the team remains focused on delivering the agreed-upon product.
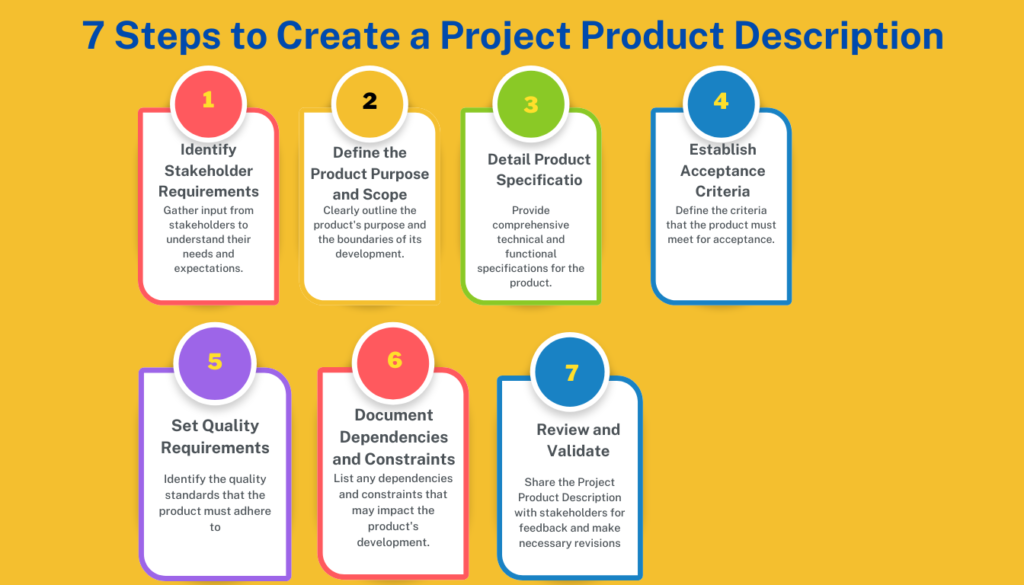
Key Components of a Project Product Description
| Steps to Create a Project Product Description | Description |
|---|---|
| Identify Stakeholder Requirements | Gather input from stakeholders to understand their needs and expectations. |
| Define the Product Purpose and Scope | Clearly outline the product’s purpose and the boundaries of its development. |
| Detail Product Specifications | Provide comprehensive technical and functional specifications for the product. |
| Establish Acceptance Criteria | Define the criteria that the product must meet for acceptance. |
| Set Quality Requirements | Identify the quality standards that the product must adhere to. |
| Document Dependencies and Constraints | List any dependencies and constraints that may impact the product’s development. |
| Review and Validate | Share the Project Product Description with stakeholders for feedback and make necessary revisions. |
Steps to Create a Project Product Description
Planning the Next Stage
Once the initial groundwork is laid, it is crucial to plan the next stage of the project. This involves creating detailed plans that outline how the project will be managed and executed moving forward. Proper planning ensures that the project stays on track, meets its objectives, and delivers value to stakeholders.
What is Planning the Next Stage?
Planning the next stage involves developing a comprehensive plan that covers all aspects of the upcoming project phase. This includes defining tasks, allocating resources, setting timelines, and establishing processes for monitoring and control. The goal is to ensure a smooth transition from the Project Start-Up phase to the execution phase.
Key Components of Planning the Next Stage
| Key Components of Planning the Next Stage | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Defining Tasks and Activities | Break down the project into smaller, manageable tasks and activities. | Helps in organizing the work and ensuring that all necessary tasks are identified and planned for. |
| Allocating Resources | Assign resources, including team members, equipment, and budget, to each task. | Ensures that resources are used efficiently and are available when needed. |
| Setting Timelines | Develop a detailed schedule that outlines when each task will be started and completed. | Provides a clear timeline for the project and helps in tracking progress. |
| Establishing Monitoring and Control Processes | Define processes for tracking progress, managing risks, and making adjustments as needed. | Ensures that the project stays on track and any issues are addressed promptly. |
| Communication Plan | Develop a plan for how information will be shared among the project team and stakeholders. | Ensures that everyone is informed and aligned throughout the project. |
Steps to Plan the Next Stage
- Review Initial Plans and Documents: Start by reviewing the Project Brief, Outline Business Case, and other initial documents to ensure alignment with project goals.
- Break Down the Work: Create a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to identify all tasks and activities required for the next stage.
- Resource Allocation: Assign resources to each task, ensuring that team members and other resources are available and properly allocated.
- Develop a Detailed Schedule: Use project management tools to create a detailed schedule, outlining start and end dates for each task.
- Establish Monitoring and Control Processes: Define how progress will be tracked, how risks will be managed, and how changes will be handled.
- Create a Communication Plan: Outline how information will be communicated, including the frequency and methods of communication.
Approval and Authorization

Obtaining approval and authorization is a critical step that marks the transition from planning to execution. This step ensures that all key stakeholders are aligned, the project is feasible, and there is a formal commitment to proceed.
What is Approval and Authorization?
Approval and authorization involve securing formal consent from stakeholders to move forward with the project. This includes the endorsement of the Project Brief, Outline Business Case, and other foundational documents. It ensures that the project has the necessary backing and resources to proceed to the next stage.
Best Practices for a Successful Project Start-Up
| Best Practices for a Successful Project Start-Up | Description | Importance | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clearly Define Objectives and Scope | Establish clear and specific project objectives and define the project scope to prevent misunderstandings and scope creep. | Ensures that all stakeholders have a common understanding of what the project aims to achieve and what is included or excluded. | Develop a detailed Project Brief outlining objectives, scope, and deliverables. |
| Engage Stakeholders Early | Involve stakeholders from the beginning to gather input, build trust, and secure buy-in. | Helps in understanding stakeholder needs and expectations, leading to better project alignment and support. | Conduct stakeholder meetings and workshops to discuss project goals and gather feedback. |
| Develop a Comprehensive Project Plan | Create a detailed project plan that covers all aspects of the project, including tasks, resources, timelines, and risks. | Provides a clear roadmap for project execution, ensuring that all tasks are identified and planned for. | Use project management tools to develop and document the project plan. |
| Conduct a Feasibility Analysis | Assess the feasibility of the project in terms of technical, financial, and operational aspects. | Ensures that the project is practical and achievable within the available resources and constraints. | Develop an Outline Business Case to evaluate the project’s viability. |
| Identify and Mitigate Risks Early | Conduct an initial risk assessment to identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies. | Helps in proactively addressing risks before they impact the project. | Create a risk register and regularly update it throughout the project lifecycle. |
| Establish Clear Roles and Responsibilities | Define the roles and responsibilities of all team members and stakeholders to ensure accountability and effective collaboration. | Prevents confusion and ensures that everyone knows their specific duties and who to report to. | Develop an organizational chart or RACI matrix (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) to document roles. |
| Develop a Communication Plan | Create a plan for how information will be shared among the project team and stakeholders. | Ensures that everyone is informed and aligned throughout the project, facilitating better collaboration and decision-making. | Outline communication methods, frequency, and responsible parties in a communication plan. |
| Secure Formal Approval and Authorization | Obtain formal approval and authorization from stakeholders to proceed with the project. | Ensures that the project has the necessary backing and resources to move forward. | Present the Project Brief and Outline Business Case for approval and obtain formal sign-off. |
Personal Experience, Insights and Reflections
- Adaptability in Methodologies
- Throughout my career, I have learned the importance of being adaptable with project management methodologies. Whether using Agile for its flexibility or Waterfall for its structured approach, the key is to choose the methodology that best fits the project requirements and team capabilities.
- Importance of Stakeholder Communication
- Consistent and clear communication with stakeholders is crucial. I have found that keeping stakeholders informed and involved through regular updates and meetings helps to build trust and ensures that everyone is aligned with the project’s objectives.
- Value of Comprehensive Risk Management
- Proactively identifying and managing risks has been a cornerstone of my project management approach. Creating a detailed risk management plan and regularly updating the risk register has helped mitigate potential issues before they escalate, ensuring smoother project execution.
- Team Empowerment and Collaboration
- Empowering team members and fostering a collaborative environment leads to better outcomes. I have always prioritized creating a culture where team members feel valued and are encouraged to share their ideas and take ownership of their tasks.
- Leveraging Technology and Tools
- Utilizing project management tools like Microsoft Project, Jira, and collaborative platforms has significantly enhanced my ability to manage complex projects. These tools have improved task tracking, communication, and overall project visibility, leading to more efficient project management.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement
- Embracing a mindset of continuous learning and improvement has been vital. Each project presents unique challenges and opportunities for growth. Reflecting on lessons learned and applying these insights to future projects has been instrumental in refining my project management skills and achieving better results.
Conclusion
A successful Project Start-Up phase is essential for setting the foundation of any project. By meticulously defining objectives and scope, engaging stakeholders, developing comprehensive plans, and securing formal approval, project managers can ensure that their projects are well-positioned for success. The practices highlighted in this blog post are designed to help project managers navigate the complexities of the start-up phase, minimizing risks and maximizing efficiency.
Final Thoughts
The Project Start-Up phase is not just a preliminary step but a critical foundation for the entire project lifecycle. By adhering to the best practices outlined in this post, project managers can create a robust framework that supports effective execution and successful project outcomes. Remember, the time and effort invested in the start-up phase can significantly influence the overall success of the project.
In conclusion, a well-executed Project Start-Up phase sets the stage for achieving project objectives, meeting stakeholder expectations, and delivering value. By following the guidelines provided, project managers can lead their teams with confidence and drive their projects to successful completion.
Call to Action
If you found this blog post on Project Start-Up helpful, don’t forget to subscribe to our newsletter for more insightful articles and updates on project management best practices. Stay informed with the latest tips and strategies to enhance your project management skills.
Join the Community: Share this post with your colleagues and fellow project managers to spread the knowledge and encourage effective project start-up practices. Let’s collaborate and achieve project excellence together!
Stay Connected: Follow us on social media for real-time updates, engaging discussions, and more resources to help you succeed in your project management journey.
Take the Next Step: Implement the best practices outlined in this post and see the positive impact on your projects. Start your next project with a strong foundation and drive it to successful completion.
FAQ
What is the Project Start-Up phase?
The Project Start-Up phase is the initial phase in project management where foundational activities are conducted to ensure the project’s feasibility, alignment with organizational goals, and readiness for execution. This phase involves defining project objectives, scope, and key deliverables, as well as securing stakeholder approval and resource allocation.
Why is the Project Start-Up phase important?
The Project Start-Up phase is crucial because it sets the foundation for the entire project. It ensures that the project has clear objectives, a well-defined scope, and the necessary stakeholder support. Proper planning during this phase helps prevent scope creep, identify potential risks, and allocate resources effectively, leading to a higher likelihood of project success.
What are the key activities in the Project Start-Up phase?
Key activities in the Project Start-Up phase include:
- Appointing key roles such as the Executive and Project Manager
- Designing the project management team
- Preparing the Project Brief
- Developing the Outline Business Case
- Creating the Project Product Description
- Planning the next stage
- Securing approval and authorization
How do you engage stakeholders during the Project Start-Up phase?
Engaging stakeholders during the Project Start-Up phase involves identifying all relevant stakeholders, understanding their needs and expectations, and involving them in key discussions and decisions. Conducting stakeholder meetings and workshops, presenting project plans, and gathering feedback are essential steps to build trust and secure buy-in.
What is the difference between the Project Start-Up and Project Initiation phases?
The Project Start-Up phase focuses on initial planning and feasibility assessment to determine if the project should proceed. It involves defining objectives, scope, and key deliverables. The Project Initiation phase, on the other hand, involves more detailed planning and preparation, including the development of comprehensive project plans and detailed schedules, based on the foundations laid during the Start-Up phase.
How do you ensure a successful Project Start-Up phase?
To ensure a successful Project Start-Up phase, it is important to:
- Clearly define project objectives and scope
- Engage stakeholders early and often
- Develop comprehensive project plans
- Conduct feasibility analyses
- Identify and mitigate risks early
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities
- Develop a robust communication plan
- Secure formal approval and authorization
What documents are typically produced during the Project Start-Up phase?
Key documents produced during the Project Start-Up phase include:
- Project Brief
- Outline Business Case
- Project Product Description
- Initial project plan
- Risk register
- Stakeholder engagement plan


